You could have the best content on the internet and still get zero traffic. Why? Because search engines can’t actually find it, read it, or figure out what to do with it.
That’s where a technical SEO audit comes in. Is your website built with SEO and search engines in mind? Technical SEO involves optimization of your website’s backend. Several tasks include this process, including improving crawlability in search engines, indexability, and user experience.
A lot of other technical things and factors play a role in this process. I’m talking about page speed, mobile compatibility, and how your URLs are structured.
We’ve seen businesses invest thousands in SEO while their site has basic technical issues. Broken links are a common thing (links that go nowhere when you click or show errors like 404 or 403). Sometimes their website pages take 20 seconds to load. It’s frustrating because these problems are fixable.
What Is a Technical SEO Audit and Why Does It Matter
We can break down SEO into three parts to make it easier to understand. On-page SEO deals with your content and keywords. Off-page SEO handles backlinks and your site’s reputation across the web. The more quality backlinks your site has, the better. Technical SEO is different. It focuses on whether search engines can properly crawl, understand, and index your website in the first place.
A technical SEO audit checks these backend elements:
- Crawlability – Google bots or crawlers consistently check for new pages and quality info on the web. Can Google’s bots access all your important pages? They can’t if your site has a messy structure or content is of poor quality. If your site has blocking rules in place, search engines might miss half your content.
- Page Speed and Mobile Performance – Slow sites frustrate users and get penalized in rankings. The ideal speed is 2.5 seconds or less for a good user experience. Mobile optimization isn’t optional anymore since most people browse on their phones. Maybe you’re reading this on mobile.
- Indexability and Structured Data – Indexability is the ability of search engines to add a website page to their databases. But what gives them this ability? It’s the content of the page and technical signals. People get confused between crawlability and indexability. Crawlability is like getting your book into Google’s library. Indexability puts it on the right shelf so people can actually find it. Structured data helps Google understand what your content is about. It can lead to rich snippets and better visibility.
For example, if you run paid campaigns through a Facebook ads marketing agency, technical issues on your site can kill conversions even when your ads perform perfectly.
A solid website technical audit identifies these weak spots before they hurt your traffic and revenue.
You need to fix the foundation first. Better content and marketing efforts will work when your technical SEO is clean and everything runs smoothly under the hood.
Step-by-Step Technical SEO Audit Checklist
Let’s get into the actual work. This technical SEO audit checklist walks through everything you need to review, why it matters, and how to fix common issues. It can be so comprehensive and sometimes boring. Professionals take years to master them. So, to keep it simple and easier to implement, we’ve listed information in the most straightforward way possible.
Step 1: Check Site Accessibility and Crawlability
Start here because if search engines can’t crawl your site, nothing else matters. Open Google Search Console and look at the coverage report. You’ll see which pages Google found and which ones it couldn’t access. This tells you immediately if there’s a crawling problem.
Next, check your robots.txt file. Type yourdomain.com/robots.txt in your browser. For example, “https://mmnovatech.com/robots.txt”. This file tells search engines which pages to crawl and which to skip. We’ve seen entire blogs hidden from Google because someone accidentally blocked the wrong section.
Here’s what to do:
- You can download Screaming Frog or use Ahrefs to crawl your site like Google does
- Look for pages returning errors or being blocked unnecessarily
- You need to find your XML sitemap at yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml. You can create sitemaps using tools like the Yoast plugin for free.
- Submit it through Search Console if you haven’t already
- Make sure your sitemap only includes pages you want indexed
Your sitemap is basically a roadmap for search engines. Keep it clean. It will be better to use a plugin like Yoast or a reliable sitemap-generating website. It will save you a lot of time, and you will avoid errors in listing pages. It will take only a few minutes to generate. This is an important part of this technical seo checklist.
Step 2: Review Site Indexation
Now check if Google is actually indexing your pages. This matters because you could have a hundred great blog posts, but if Google isn’t indexing them, they won’t rank.
Go to Google and search site:yourdomain.com. This shows every page Google has in its index.
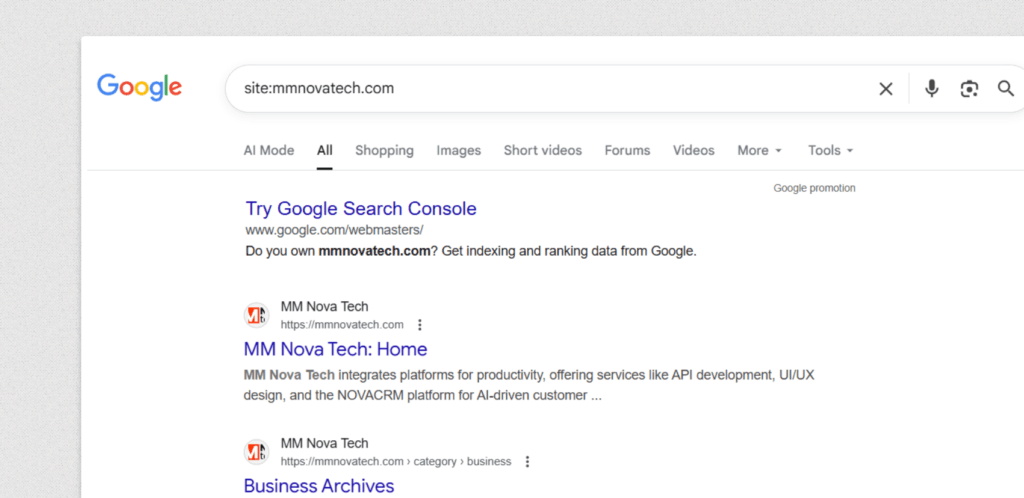
Compare that number to how many pages your site actually has. Big difference? You’ve got a problem.
Head to Google Search Console and click the Index Coverage report. You’ll see pages that are indexed, excluded, or have errors. Look for pages marked “noindex” that shouldn’t be. Sometimes old settings from a site migration or staging environment block new content from appearing in search results. That is a bit complex SEO thing; you’d better have an SEO expert or agency take care of it.
Step 3: Analyze Website Speed & Core Web Vitals
Page speed isn’t just about user experience anymore. Google uses Core Web Vitals as a ranking factor. These are basically metrics that Google uses to check how fast, stable, and smooth your site feels. Slow sites rank lower. Run your site through PageSpeed Insights. Google will score your mobile and desktop performance, plus give you specific suggestions. Pay attention to three metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – How fast your main content loads. Should be under 2.5 seconds.
- Interaction To Next Paint (INP) – How quickly your site responds to clicks. Should be under 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – Whether elements jump around while loading. Lower is better.
Common fixes that can do the magic:
Images are usually the biggest problem. If your image is 3mb instead of 200kb, it’s destroying the load speed. You can use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to compress them.
If you’re planning a redesign or optimization project, make sure you’re working with the right team. Here’s a detailed guide on how to find the right web developer.
Step 4: Ensure Mobile-Friendliness
Have you checked your website’s mobile interface? Google uses mobile-first indexing now (since 2016, to be specific). That means it looks at your mobile site first when deciding how to rank you. If your mobile experience is broken, your rankings suffer even for desktop searches.
Test your site on your phone right now. Does everything work? Can you click buttons easily? Is the text readable without zooming? These aren’t hypothetical questions. You need to get practical answers.
Google Search Console has a Mobile Usability report that flags specific issues. Use it.
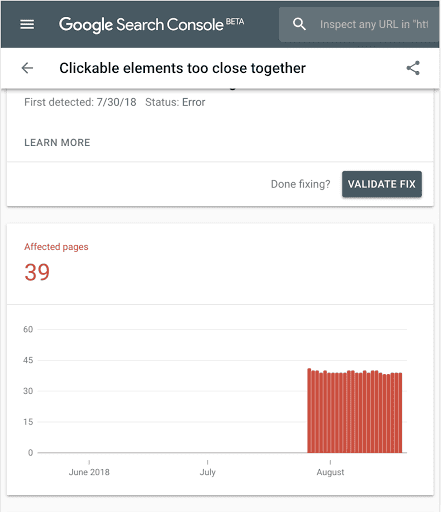
Also, run your URL through Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool. It shows you exactly what Google sees on mobile. Common problems include text that’s too small. Sometimes there are clickable elements too close together. These are easy fixes that make a real difference.
Step 5: Fix Broken Links & Redirects
We’ve talked a little about broken links earlier. So they are not really amusing things. You click on a link and it doesn’t work. How do you describe it? It’s a ‘broken link’. Every 404 error is a dead end where link equity disappears.
The best part is that you don’t need to manually look for such links. Nor do you need to wait for users complaining about broken links. You can use Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or SEMrush Site Audit to find broken links. You’ll see both internal links (between your own pages) and external links (to other sites). You can then fix broken links immediately by updating the URLs or removing them.
Watch out for redirect chains. This is a bit strange but it happens. That’s when one URL redirects to another, which redirects to another. Google doesn’t like following multiple redirects. It slows down crawling. Users don’t like it either. Clean these up so redirects go straight to the final destination.
Step 6: Optimize Site Architecture & URL Structure
Your site structure should make sense to humans and search engines. Important pages should be easy to reach. You don’t want your main service page to be hidden from audience.
If someone has to click through seven pages to find your main service offering, that’s a problem. Google thinks it’s not important either.
URL best practices:
- Keep them short and descriptive
- Use hyphens between words
- Avoid random numbers or parameters when possible
- A URL like /services/web-design beats /page?id=12345 every time
Implement breadcrumb navigation. It’s like the navigation you see when finding files on a local computer. It helps users understand where they are on your site. It also helps Google understand your site hierarchy. This is part of a solid SEO audit checklist because structure directly affects how well your content performs.
Step 7: Review On-Page SEO Elements
This is a bit technical audit. You need to check page SEO elements because they’re part of how search engines understand your content.
Title tags and meta descriptions
Each page needs a unique, descriptive title under 60 characters. Meta descriptions should be compelling and under 160 characters. That’s your moment to hook someone in under 160 characters. These don’t directly affect rankings but they influence whether people actually click your result.
Heading structure
Each page should have one H1 tag. Subheadings should follow a logical hierarchy with H2s, H3s, and so on. This isn’t just for SEO. It makes your content scannable. But it also makes your content more organized and search engines love it.
Images and alt text
Alt text matters for accessibility and helps Google understand your visuals. Describe what’s in the image naturally. Don’t stuff keywords.
Internal linking strategy
Are you linking to important pages from multiple places? This distributes link equity and helps search engines discover content. If you’re working with a social media marketing agency, you need to align your SEO strategy with your social media strategy. Aligning your on-page SEO and social strategies ensures consistent visibility across search and social.
Your Site Deserves Better
Most websites are sitting on fixable problems that cost them traffic every single day. A proper website SEO audit shows you exactly what’s holding you back. It’s maintenance work that protects your rankings and visibility.
You don’t need to be a developer or hire an expensive agency right away. This technical SEO audit checklist will walk you through the key areas to check. And if your brand also relies on paid or organic growth, working with an SEO marketing agency can help identify and fix these issues at scale.
You can start with crawlability and site speed today. Pick one section today and fix what you find. Your competitors aren’t waiting. And if you need help, we are waiting for your call or email.